In this post, I want to share some insights gained from my advisory engagements on cloud spend. I advised over 20 companies on cloud cost optimization. Unfortunately, what we envisaged to be short-term engagements where I'd analyze bloating costs and then share tips and tricks ended up being multi-quarter engagements requiring continued support. This was highly inefficient!
How did we end up here?
To answer this, let’s take a step back and examine our DevOps practices and tools in more detail.
Endless audit loops…
While investigating cloud spend, we would dig through spend dashboards, discover insights, sort them through priorities, assign to teams, and then measure them again - every week. The toil it took on teams was immense. It was like Groundhog day.
We had success on many occasions and celebrated the pure dollar savings. However, this really made me question our fundamental approach- how can we think preemptively about this?
Make no mistake, continuous verification and auditing is an absolutely necessary practice. We all need to routinely audit costs and practices, but it should not be the only way.
Expanding on this, I realized that it isn’t limited to cloud cost. We take this "by-audit’" approach in almost all of our DevOps practices.
The by-audit approach
I call this approach of taking stock retrospectively as 'by-audit'. These days when I come across a DevOps tool or process, I classify whether it fixes things "by-audit" or "by-design".
Let’s look closer at how we approach practices when you think by-audit:
- Compliance : You perform quarterly/annual audits, retrieve the non-compliances and try to isolate which teams they belong to and assign them for fixing. It doesn't guarantee the same issues won't be back in the next audit.
- Security : Higher than required privileges, open database credentials, improper network segmentation, and security groups are common areas where you pull reports out and try to figure out with teams whether they are genuine or misconfigurations.
- Disaster Recovery : Many companies set up simple backups and runbooks on how to recover from disasters and the confidence in these is usually low. So the DevOps team either live with blind optimism hoping for the best or, on the other extreme, live in abject fear and perform DR drills several times in a quarter because they are paranoid that the runbook will drift.
- Completeness around Monitoring : There is always this lack of confidence whether the required dashboard and alerts are complete or not or whether the right team is being notified or not. It’s a guessing game. So as issues happen, we jump into a process of checking all dashboard and alert configurations. We wrote an article on this here.
This applies to tools as well.
For instance, let's consider you have a tool that analyzes exposed credentials of a database. A database expert then analyzes the report. The expert identifies the services connecting to the database, finds the owners for it and informs them so they can re-examine it.
Think by-design
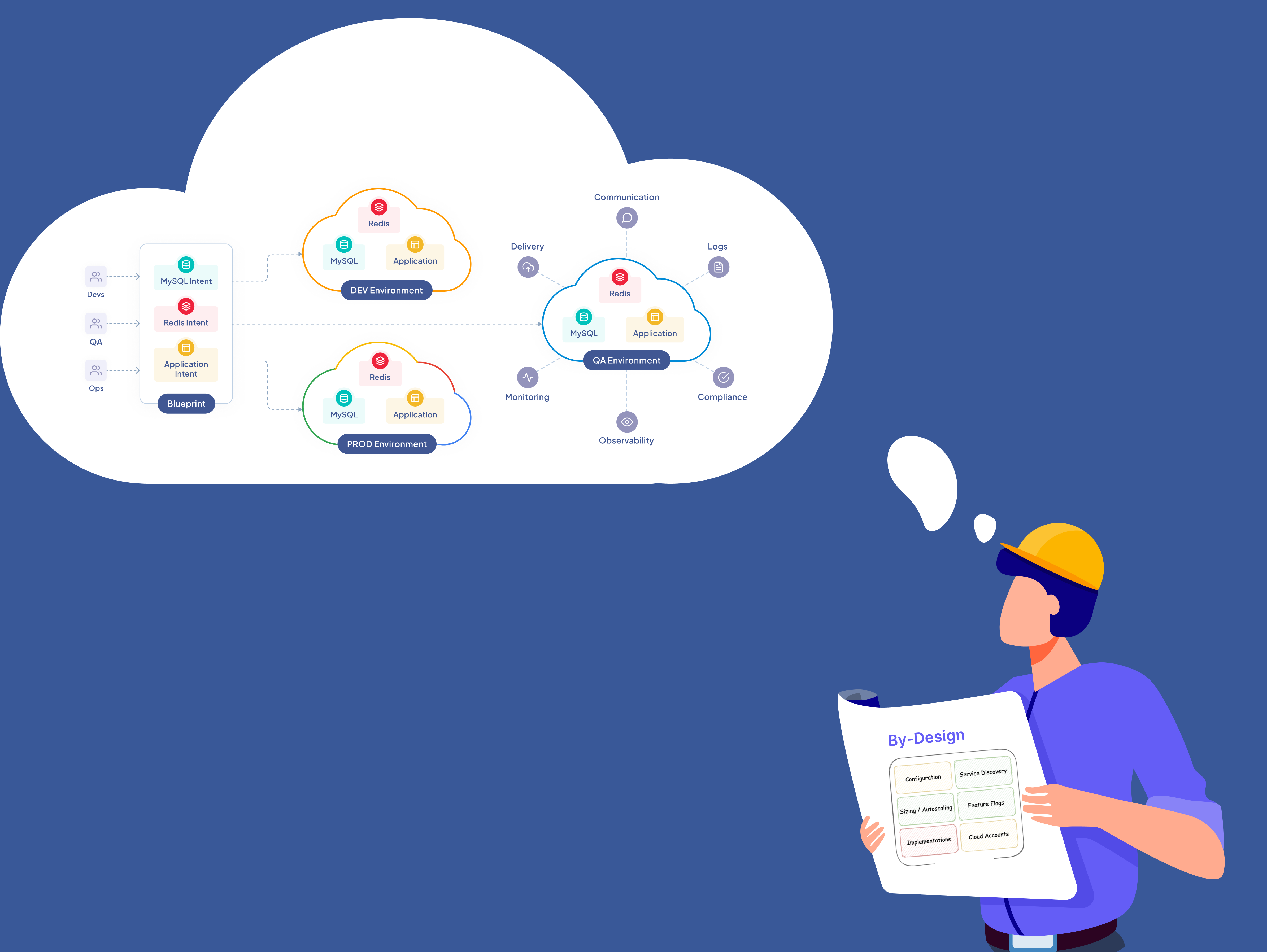
With the "by-design" approach we ensure adoption of best practices and principles before implementation.
To continue the above example of the credentials for the database, a "by-design" approach would ensure that there is a formal way to request a credential for each of the services beforehand.
Also, it would require you to ensure that there is a policy on credential creation, isolation, storage, and rotation which is applied uniformly when this is fulfilled, programmatically. It must also be important to ensure that this is the only way credentials can be created.If the above is taken care by design, the need of verification tools will go down significantly. The codified policy and code can be statically verified and can be moved upstream to the CI pipeline.
Similarly, with AWS Cost Explorer, where you analyze costs per team and identify teams consuming the most resources, it is a "tool of verification".
While AWS Budgets, where you allocate budgets for a team combined with automation that prevents teams to go over budget, will be a "tool of design".
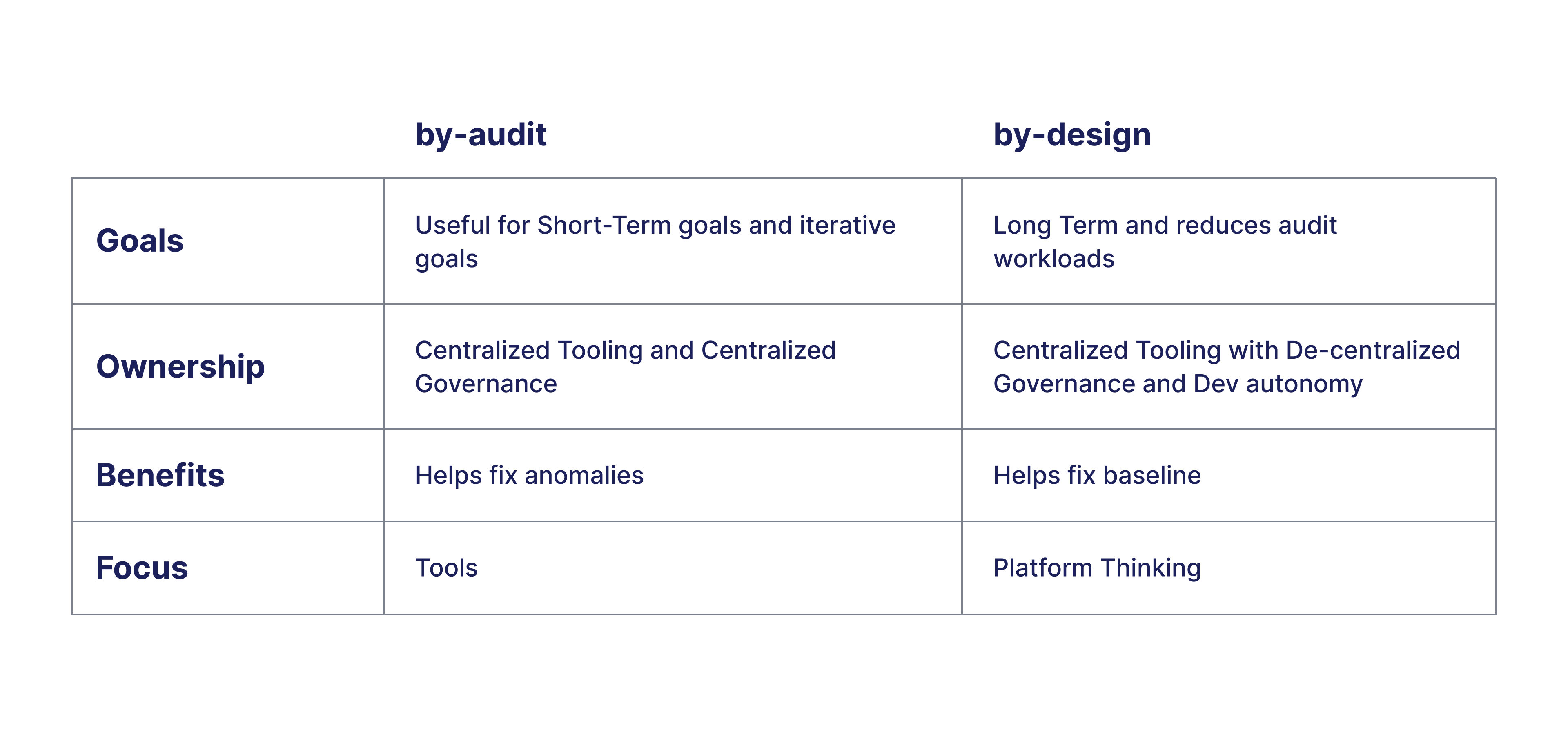
Comparison of by-Audit versus by-design
 Let’s expand on these.
Let’s expand on these.
Goals
If you have a burning problem like cost bloating, then the by-audit process comes in handy. You would need to put a team together, pull out all reports, break them down and assign them to developers to fix them. However, more often than not, these practices become the norm. By-design processes provide long-term benefits and ensure things stay fixed. You may need audits still, but the workload dramatically reduces.
Ownership
Typically, a central team is responsible in the by-audit approach. Here, the governance is said to be centralized, because ownership is with one team. Generally, they use certain tools and analyze reports. This is fine for the short term.
However, with the by-design approach the goals are long-term. Ownership is given to multiple teams so governance is de-centralized and teams get more autonomy. This ensures clear ownership boundaries so that every team is aware of their share of tasks.
Benefits
Apart from routine audits, usually, by-audit processes are useful in case of anomalies e.g. a security breach or a cost spike. While it's easy to tackle these anomalies with audits, it's not sustainable for improving baselines. By-design processes ensure that the baseline improves overall - i.e. your default security posture, observability coverage, and cost baselines.
Focus
While moving from by-audit to by-design processes, the focus must shift from Tools to Platform thinking. The questions that need to be answered are :
- How will this tool be used by the developers directly without additional cognitive load on them?
- How will this tool integrate earlier in my delivery pipeline so the mistakes don't propagate to production?
Conclusion
Platform teams of today must shift from stitching tools and audit-driven practices. Indeed, Platform engineering is centered around a by-design mindset.
Platform teams need to think about how to devise ways where the well-architected aspects of cloud and practices are 'ensured' and not required to be audited.